What is the difference between slag and fly ash?
Supplementary cementitious materials (SCM) are usually incorporated into the composition of modern concrete. These materials are often by-products of other industrial processes or natural materials. Among them, some materials need to be further processed to be suitable for concrete. Some of these materials have gelling properties themselves; in addition, there are some materials that do not have gelling properties themselves, which we call pozzolanic materials.
Slag powder and fly ash are the two most widely used auxiliary cementitious materials in the concrete industry. Today, most concrete is produced with one or both of these materials incorporated. Because of this, their properties are frequently compared with each other by concrete technicians to find the best concrete mix.
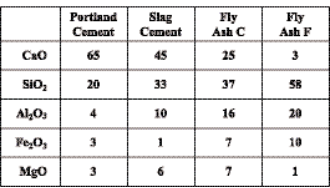
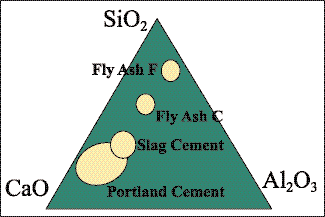
Fig.1 Ternary phase diagrams of oxides in different cementitious materials
As shown in the ternary phase diagram in Figure 1, the chemical composition of slag powder is closer to Portland cement than fly ash. This is also one of the reasons why slag powder can be used in concrete in a large amount. Both slag powder and fly ash can partially replace Portland cement in concrete. In ordinary concrete, the content of slag powder can be as high as 50% (in some special applications, such as mass concrete, the content of slag powder can reach 80%). The content of fly ash is usually controlled between 20% and 30%.
Slag powder is a by-product of the ironmaking process, and the entire process is strictly controlled, so its chemical composition remains relatively stable even if the source of raw materials fluctuates. Fly ash is a by-product of pulverized coal combustion in coal-fired power plants, and the difference in raw materials will directly lead to fluctuations in the chemical composition of fly ash.
Compared with fly ash, the chemical composition of slag powder fluctuates less. Therefore, the quality stability of concrete mixed with slag powder is better than that of concrete mixed with fly ash.
1. The effect of the two on the performance of plastic concrete
1) Water Reduction: The use of both materials reduces the amount of water required for the concrete to achieve the specified flow properties. The reason why slag powder has a water-reducing effect is that it can affect the properties of the slurry and its adsorption properties. (Weishen New Materials: The particle gradation of the slag powder is reasonable, and if the dosage is appropriate, it has a certain water-reducing effect. This is because the microscopic shape of the slag powder is an irregular glass body, and its adsorption to water is higher than that of silicate. Cement is smaller and shows a certain degree of water reduction.) For fly ash, it is mainly because of its better morphological effect and size effect (WeiShen New Materials: fly ash is in the form of spherical glass beads , play the role of a ball bearing, thus showing a certain water reduction). Therefore, this makes these two materials have a certain degree of water reducing effect on the concrete mixture.
2) Air content: There are many different factors that affect the air content of concrete. The difference in carbon content in fly ash is a major factor causing the fluctuation of concrete air content. Slag powder does not contain carbon, so it will not affect the stability of concrete air content.
3) Setting time: The mixing of slag powder and fly ash in concrete will affect the initial setting time of concrete. The setting time of concrete mixed with slag powder is shorter than that of concrete mixed with fly ash
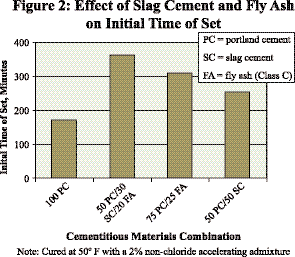
Fig.2 Effect of slag powder and fly ash on initial setting time
4) Pumpability and light-receiving properties: The mixing of slag powder and fly ash into concrete is equivalent to filling the voids of concrete with fine particles, so the pumpability and light-receiving properties of concrete can be greatly improved.
2. The influence of the two on the hardening performance of concrete
1) Strength: The 28-day strength of concrete mixed with slag powder and C-grade fly ash is higher than that of cement concrete mixed with F-grade fly ash.
2) Permeability: Under the normal specified dosage, tested according to ASTM 1206 (Rapid Chloride Ion Penetration Test) standard, the concrete mixed with slag powder has a lower performance than the concrete mixed with Class F or Class C fly ash. permeability.
3) Sulfate erosion and alkali-aggregate reaction: mixing slag powder and F-class fly ash can protect concrete from sulfate erosion and alkali-aggregate reaction damage. Class C fly ash may not have this capability.
4) Color: Concrete mixed with slag powder has lighter color and higher reflectivity than Portland cement concrete. The C-grade fly ash and F-grade fly ash will make the concrete appear light yellow or dark gray, respectively.
Disclaimer: As with all concrete, multiple batches of testing should be performed to verify concrete performance. Test results may vary depending on factors such as ambient temperature, mixture components, etc. It is recommended that you consult a slag powder professional for assistance. Nothing contained herein should be taken or construed as a warranty, express or implied, including any warranty of fitness for a particular purpose.
